Long title: Act On The Reorganisation Of The Safety Of Technical Work Equipment And Consumer Products of 6 January 2004
All rights in this translation are held by the Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz und Arbeitsmedizin, Friedrich-Henkel Weg 1-25, 44149 Dortmund, Germany. No liability is assumed for translation mistakes. The German original as published in the Bundesgesetzblatt is authoritative.
The Bundestag has, with the consent of the Bundesrat, resolved to adopt the following Act:
Article 1
Act on Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products (Equipment and
Product Safety Act - GPSG)*)
*) The purpose of this Act is to implement
In addition this Act serves to implement
Chapter 2 Bringing Products into Circulation and Marking of Products
Chapter 3 Surveillance of the Bringing into Circulation of Products
Chapter 5 Installations Subject to Mandatory Inspection
Chapter 6 Regulations Governing Criminal Penalties and Administrative Fines
Chapter 7 Concluding Regulations
(1) This Act governs the bringing into circulation and display of products as implemented independently within the framework of an economic enterprise. The Act does not apply with respect to the bringing into circulation and display of used products which
This Act also does not apply with respect to the bringing into circulation and display of technical work equipment intended by its very nature exclusively for use for military purposes.
(2) The present Act also applies to the erection and Operation of installations subject to mandatory inspection which serve commercial or economic purposes or which may endanger employees, with the exception of the installations subject to mandatory inspection
(3) The regulations of the present Act aimed at ensuring safety and health during the bringing into circulation or display of products shall not apply where other statutory regulations lay down equivalent or more extensive requirements regarding the guarantee of safety and health. Sections 5, 6 and 8 to 10 shall not apply where other statutory regulations lay down equivalent or more extensive provisions.
(4) Statutory regulations which serve to ensure safety and health during the use of products shall not be affected; this applies in particular with respect to regulations which impose such an Obligation on the employer.
(1) Products are
(2) Technical work equipment encompasses ready-to-use working devices whose intended use is exclusively for work purposes, their accessories and protective equipment which are not part of a working device, and parts of such technical work equipment if these are covered by a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 1 or 2.
(3) Consumer products are commodities and other products which are intended for consumers or which may be used by consumers under reasonably predictable conditions even when not intended for them. Consumer products also include commodities and other products made available to the consumer when a Service is being rendered.
(4) Working devices and commodities are ready for use when they can be used as intended without the need to add further parts. Working devices and commodities are also ready to use when
(5) Intended use is
(6) A predictable incorrect use is the use of a product which is not envisaged by the party bringing it into circulation but which may arise from the reasonably predictable behaviour of the anticipated individual user.
(7) Installations subject to mandatory inspection are
Such installations also include measuring Instrumentation, control equipment and regulating devices intended to ensure safe Operation of the Installation. The installations subject to mandatory inspection as described in the numbers 2, 3 and 4 do not include the energy installations in the meaning of Section 2 Subsection 2 of the Energy Industry Act. Installations subject to mandatory inspection are equivalent to products in the meaning of Subsection 1 where they are not already covered by Subsection 1.
(8) Bringing into circulation is any passing on of a product to another party regardless of whether the product is new, used, reworked or has been substantially modified. Importation into the European Economic Area is the equivalent of the bringing into circulation of a new product.
(9) Display is the displaying or presentation of products for advertising purposes.
(10) Manufacturer is any natural or legal person who
A manufacturer is deemed to be any person who applies his name, his trademark or some other distinguishing mark to a product for business purposes and therefore presents himself as the manufacturer, or who influences the safety characteristics of a consumer product as any other kind of person bringing a product into circulation.
(11) Authorised representative is any natural or legal person based in the European Economic Area who is authorised in writing by the manufacturer to act on his behalf.
(12) Importer is any natural or legal person based in the European Economic Area who Imports a product from a third country into the European Economic Area or who arranges for such Import.
(13) Dealer is someone who brings a product into circulation for business purposes and is not the manufacturer in the meaning of Subsection 10, authorised person in the meaning of subsection 11 or importer in the meaning of Subsection 12.
(14) Delegated body is the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, subject to any different Provision of a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 4.
(15) Approved bodies are
(16) Harmonised Standard is a non-binding technical specification which has been accepted by a European Standards Organisation in accordance with the procedures laid down in the Directive 98/34/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 22 June 1998 concerning an Information procedure in the area of Standards and technical regulations (OJ EC No. L 204 p. 37) and whose source has been published in the Official Journal of the European Communities.
(17) Recall is any measure aimed at causing the return by the user of a product already in circulation.
(18) Taking back is any measure intended to prevent a product from being sold, displayed or offered to the user.
(1) The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour may, in consultation with the Federal Ministry of Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture, the Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety, the Federal Ministry of Defence and the Federal Ministry of Transport, Construction and Housing, adopt ordinances under the provisions of Sentence 2 for products after a hearing by the Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products with the consent of the Bundesrat (upper house of parliament) in order to fulfil obligations arising form inter- governmental agreements or to implement or perform the statutory regulations passed by the European Communities. A statutory ordinance under Sentence 1 can govern the following:
(2) The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour may, in consultation with the Federal Ministry of Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture, the Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety, the Federal Ministry of Defence and the Federal Ministry of Transport, Construction and Housing, adopt ordinances under the provisions of Sentence 2 for products after a hearing by the Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products with the consent of the Bundesrat (upper house of parliament), adopt statutory ordinances for products which do not fall under a statutory ordinance under Subsection 1 in order to regulate bringing into circulation or display of such products under the provisions of Sentence 2. Statutory ordinance under Sentence 1 can govern the following:
(3) The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour may, after a hearing by the Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products and with the consent of the Bundesrat, also specify in greater detail by statutory ordinance requirements for approved bodies with respect to the following in order to implement or perform the statutory regulations passed by the European Communities:
(4) By statutory ordinance without the consent of the Bundesrat tasks which have been assigned to the delegated body within the framework of the present Act may be assigned to another federal authority which has been entrusted with tasks in the field of equipment and product safety. The statutory ordinance shall be adopted by the Federal Ministry to whose operational domain the federal authority belongs in consultation with the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour.
(5) Statutory ordinances under Subsection 1 or 2 may be adopted without the consent of the Bundesrat in urgent cases or if this is necessary to ensure the immediate implementation or performance of statutory acts of the European Communities; such ordinances shall cease to be effective at the latest six months after they have come into effect. Their validity can only be extended with the consent of the Bundesrat.
(1) Where a product falls under a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 1, it may only be brought into circulation if it satisfies the requirements specified there regarding safety and health and other conditions for its being brought into circulation and the safety and health of the users or third parties or other legal assets mentioned in the statutory ordinances according to Section 3 Subsection 1 are not endangered with intended use or predictable incorrect use. If a Standard which implements a harmonised Standard satisfies one or more requirements regarding safety and health, it shall be assumed for a product manufactured in accordance with this Standard that it meets the relevant requirements regarding safety and health.
(2) Where a product is not subject to Section 4 Subsection 1 it may only be brought into circulation if it is such that, with intended use or predictable incorrect use, the safety and health of users or third parties are not endangered. When assessing whether a product meets the requirement of Sentence 1 the following must be considered in particular:
When assessing whether a product satisfies the requirements according to Sentence 1, Standards and other technical specifications may be referred to as a basis. If a Standard or other technical specification which has been determined by the Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products and published by the delegated body in the Bundesanzeiger (Federal Gazette) satisfies one or more requirements regarding safety and health, it shall be assumed for a product manufactured according to this Standard or other specification that it satisfies the relevant requirements regarding safety and health.
(3) In the case of an item of technical work equipment covered by statutory ordinances according to Section 3 Subsection 1, the legal Situation at the time it is first brought into circulation in the European Economic Area shall govern. Sentence 1 also applies for a consumer product where it is covered by statutory ordinances according to Section 3 Subsection 1. In the case of an item of technical work equipment not covered by a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 1, the legal Situation at the time it is first brought into circulation within the scope of the present Act shall govern. When a consumer product is brought into circulation which does not fall under a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 1, the legal Situation at the time it is brought into circulation shall govern.
(4) Where no different provisions are laid down in the statutory ordinances according to Section 3 the following shall apply:
(5) A product which does not satisfy the conditions according to Subsection 1 or 2 may be displayed if a visible sign clearly indicates that it does not meet these conditions and may only be purchased when the appropriate conformity has been established. In a demonstration the necessary precautions must be taken to protect persons.
(1) The manufacturer, his authorised representative and the importer of a consumer product must perform the following within the framework of their business activity:
(2) The manufacturer, his authorised representative and the importer must each notify the competent authority without delay in accordance with Annex l of the Directive 2001/95/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 3 December 2001 on general product safety (OJ EC No. L 11 P. 4) if they know or, on the basis of Information in their possession or their experience, they have concrete indications that a consumer product they have brought into circulation represents a danger to the health and safety of persons; in particular they must give notification of measures they have taken to ward off this danger. Notification under Sentence 1 may not be used for a criminal prosecution of the notifying party or for proceedings against the notifying party under the Act relating to administrative infringements.
(3) The dealer must help ensure that only safe consumer products are brought into circulation. In particular he may not bring a consumer product into circulation of which he
Subsection 2 applies to the dealer accordingly.
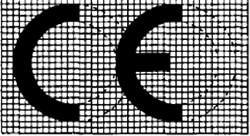
(1) It is not permitted to bring a product into circulation if it, its packing or documents accompanying it bear the CE mark even though the statutory ordinances according to Section 3 or statutory regulations do not provide for this and the conditions of Subsections 2 to 5 are not complied with.
(2) The CE mark must be applied so as to be visible, legible and permanent.
(3) The CE mark consists of the letter "CE" in the following form:

(4) If the CE mark is reduced in size or enlarged, the proportions shown here must be maintained.
(5) In addition to the CE mark no marks may be applied which could confuse third parties with respect to the significance and form of the CE mark. Any other mark may be applied provided the visibility and legibility of the CE mark is not impaired.
(1) Provided that statutory ordinances under Section 3 do not provided for something different, technical work equipment and ready-to-use commodities may bear the GS mark (GS = "Geprüfte Sicherheit" - "Tested Safety") officially published by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour if is has been awarded by a GS body according to Section 11 Subsection 2 on application from the manufacturer or his authorised representative. The GS mark may only be awarded if the GS body
A certificate must be issued concerning the award of the GS mark. The validity of the award is limited to a maximum period of five years.
(2) The GS body according to Section 11 Subsection 2 must take inspection measures to monitor the manufacture of the technical work equipment and ready-to-use commodities and the legal use of the GS mark. If the conditions for the award of the GS mark are no longer met, the GS body shall withdraw the award. In such cases it shall notify the other GS bodies and the competent authority of the withdrawal.
(3) The manufacturer shall ensure that the technical work equipment and ready-to-use commodities he manufactures conform to the type specimen tested. He shall accept the inspection measures under Subsection 2. He may only use the GS mark and advertise with it as long as the conditions under Subsection 1 Sentence 2 are met.
(4) The manufacturer may not use or advertise with a mark which could be mistaken for the GS mark.
(1) Subject to Sentences 2 and 3, the competent authorities under State ('Land') law shall be responsible for implementing the provisions of the present chapter. If the provisions of this Act apply under Section 1 Subsection 3 in addition to provisions of other statutory regulations, the competent authorities responsible for these shall then apply. Any responsibilities regarding the implementation of the Act as assigned by other regulations shall not be affected.
(2) The competent authorities shall ensure effective monitoring of the bringing into circulation of the products and of the products brought into circulation on the basis of a monitoring approach. The monitoring approach shall encompass in particular the following:
In the case of products subject to a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 1 and bearing a CE mark, the competent authority assumes that the requirements laid down there in each case are satisfied. In the case of technical work equipment and ready-to-use commodities bearing the GS mark according to Section 7 Subsection 1, it shall be assumed that they satisfy the requirements with respect to safety and health under Section 4 Subsections 1 and 2 and other statutory regulations.
(3) The supreme State ('Land') competent authorities shall ensure co-ordination of the monitoring of the bringing into circulation of products and of products brought into circulation, the development and updating of the monitoring approach and the preparation of cross-State measures to ward off major hazards. This does not affect products for which other statutory regulations in the meaning of Section 1 Subsection 3 Sentence 1 apply.
(4) The competent authority shall take the necessary measures if it has reason to suspect that a product does not satisfy the requirements under Section 4. It is authorised in particular
The authority itself may warn the general public if other, similarly effective measures, and specifically warnings by the manufacturer, are not taken, or not in good time. It shall waive measures under Sentence 2 where suitable measures are taken to ensure that the daner associated with a product is warded off by the person responsible for bringing the product into circulation.
(5) The competent authority shall address measures under Subsection 4 primarily to the manufacturer, his authorised representative or the importer. It may also address measures to the dealer according to the relevant needs. Measures taken against any other person shall only be permissible provided that a major and present danger cannot be warded off in any other way. If the other person suffers damage from this, he shall be compensated for this provided he has no way of obtaining compensation elsewhere or his assets are not protected by the measure taken.
(6) If a product bearing a mark according to Section 7 Subsection 1 Sentence 1 does not satisfy the requirements under Section 4 Subsection 1 or Subsection 2, the competent authority shall notify the GS body which has awarded that mark and the authority according to Section 11 Subsection 2.
(7) The competent authorities and their delegated representatives are empowered to enter premises or sites in or on which products are manufactured, stored for the purpose of bringing them into circulation or displayed, to inspect the products, to test them or to have them tested, and in particular to have them put into Operation for this purpose. The persons who manufacture the product or who store or display it for the purpose of bringing it into circulation can be called upon to bear the cost of the tests under Sentence 1 if the test shows that the requirements under Section 4 are not satisfied.
(8) The competent authorities and their delegated representatives may take samples and demand specimens free of Charge.
(9) The manufacturer, his authorised representative, the importer and the dealer shall in each case accept measures under Subsection 7 Sentence 1 and Subsection 8 and shall support the competent authorities. They are obliged to provide the competent authority on demand with the information required to enable it to perform its tasks. The person thus obliged may refuse to provide information to questions if answering such questions may expose him or a related person designated in Section 383 Subsection 1 Nos. 1 to 3 of the Code of Civil Proceedings to the risk of criminal prosecution or proceedings under the Act Governing Infringements of Administrative Regulations. He shall be informed of his right to refuse information.
(10) The competent authorities and the delegated body shall inform and support one another on measures taken under the present Act. If the authorities receive information falling under the heading of business secrecy they shall safeguard its confidentiality.
(1) If the competent authority takes measures under Section 8 Subsection 4 which prohibit or restrict the bringing into circulation of the product or which order that it be taken back or recalled, it shall notify the delegated body of this, indicating the reasons. This also covers notification of a deficiency in a technical Standard according to which the product has been manufactured. The competent authority shall also notify the delegated body of measures and precautions taken concerning the bringing into circulation or use of products which represent a major hazard and which have to be notified within the joint System for the fast exchange of information on dangers with the use of consumer goods. The procedure according to Annex II of the Directive 2001/95/EC of the European Parliament and Council of 3 December 2001 on general product safety (OJ EC No. L 11 P. 4) must be observed. This also includes notification of any change or cancellation of the measures or precautions. If the mark provided for in Section 6 or the mark provided for in Section 7 has been awarded by an approved body, the competent authority under Section 11 Subsection 2 must be notified.
(2) The delegated body reviews the notifications received to check that they are complete and consistent. It passes the notifications under Subsection 1 Sentence 1 on to the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour. It informs the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour and the Federal departments responsible of notifications under Subsection 1 Sentence 2 and passes them on to the bodies responsible in the Commission of the European Communities.
(3) The delegated body informs the competent authorities and the Federal department responsible of memoranda from the Commission of the European Communities or another member state which come to its attention.
(1) The delegated body publishes Orders under Section 8 Subsection 4 Sentence 2 Nos. 2, 5 and 6 which have become indisputable or whose immediate implementation has been ordered. Personal data may only be published if it is necessary to identify the product.
(2) The competent authorities and the delegated body make available to the general public Information in their possession on hazards for user safety and health associated with consumer products; this concerns in particular Information for the Identification of consumer products, the nature of the hazards and the measures taken. Access can be granted by electronic means. The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour, in consultation with the Federal Ministry of Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture and the Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety may regulate the details of publication in an electronic Information and communication System by statutory ordinance with the consent of the Bundesrat. Deletion intervals must in particular be provided for, as must regulations which ensure that the publications remain undamaged, complete and up to date.
(3) Personal data may only be transmitted if the individual concerned has given permission or the information interests warranting protection of the general public or the third party to whom the data is transmitted outweigh the interest of the individual concerned with respect to the prevention of transmission. Before a decision is taken on transmission, the individual concerned shall be heard.
(4) Information under Subsection 2 may not be made accessible
Before a decision is taken on access, the persons concerned must be heard in the cases of Sentence 1 No. 3. Where Information transmitted is described as a Company or business secret, the competent authority or the delegated body shall assume in cases of doubt that the person so describing it is affected.
(5) If the Information the authority passes on to the general public is subsequently found to be incorrect or the underlying circumstances are found to have been incorrectly depicted, the authority shall inform the general public accordingly in the same way in which it previously passed on the Information concerned where this is necessary to safeguard the substantial concerns of public welfare or an individual concerned has a justified interest in this and applies accordingly for this.
(1) An application may be submitted to the authority responsible for recognition as an approved body. This authority checks whether the requirements of the statutory ordinance under Section 3 Subsection 3 are satisfied. An accreditation based on harmonised Standards may be taken into account within the scope of an accreditation procedure according to Sentence 2. If the conditions are met, the authority responsible for the delegated body shall appoint the applicant as approved body for certain products and processes.
(2) A body is to be appointed by the authority responsible for the delegated body as a GS body for a certain area of work if it has been found by the competent authority in a recognition procedure that compliance with the requirements of the statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 3 is guaranteed.
(3) A body based in another member state of the European Union or another treaty state that is party to the Agreement on the European Economic Area can be appointed by the authority responsible for the delegated body as a GS body for a certain area of work. The condition for such appointment is
The administrative agreement must regulate the following:
(4) The delegated body shall publish a notice naming the approved body.
(5) The competent authority monitors compliance with the requirements given in Subsections 1 and 2. It may demand of the approved body and its personnel who are assigned the management and implementation of the specialist duties necessary Information and other support and issue the Orders required for this purpose. The competent authorities and their delegated representatives are empowered to enter and inspect the sites and business premises and the testing laboratories during the operational and business hours and to demand presentation of documents for the issuance of the certificates. Those obliged to prove Information shall accept the measures according to Sentence 3. They may refuse Information with respect to those questions which, if answered, could expose them or a related person designated in Section 383 Subsection 1 Nos. 1 to 3 of the Code of Civil Proceedings to the risk of criminal prosecution or proceedings under the Act Governing Infringements of Administrative Regulations. They shall be informed of their right to refuse Information.
(6) The authorities responsible for monitoring the bringing into circulation may demand of the approved body and its personnel assigned to the management and implementation of the specialist duties the Information and documents needed for the Performance of its tasks. Where they become involved according to Sentence 1 they shall notify the authority responsible for the recognition procedure according to Subsection 1.
(1) Within the scope of its general research commission, the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health determines and evaluates preventively safety risks and health risks which may arise in connection with products and puts forward proposals for their reduction.
(2) In individual cases the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, in consultation with the competent authorities, undertakes risk evaluations on products for which there are sufficient indications that there is an immediate danger or major risk to safety and health. It notifies the competent authority without delay of the result of the assessment and, in consultation with the latter, the parties concerned who are bringing the product into circulation.
(3) In individual cases the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health undertakes risk evaluations on products on its own responsibility where this is required in terms of conscientious action towards the bodies of the European Communities.
(4) The Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Supports the competent authority in the development and implementation of the monitoring approach in accordance with Section 8 Subsection 2, in particular by conducting a scientific analysis of deficiencies in condition of the products ascertained as measures are taken according to Section 8 Subsection 4 and by notifying the competent authority and the Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products regularly on the state of knowledge.
(1) At the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour a "Committee for Technical Work Equipment and Consumer Products" is in Operation.
(2) The tasks of the Committee are as follows:
(3) The Committee shall consist of expert persons from the authorities responsible for safety and health in the Federal and State administrations, from the approved bodies, from the statutory accident Insurance bodies, from the standardisation organisation Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V., from the Commission for Occupational Safety and Health and Standardisation, from the employers' federations, from the trade unions and the associations involved, especially of manufacturer and consumer associations. Membership shall be honorary.
(4) The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour, in consultation with the Federal Ministry of Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture, shall appoint the members of the Committee and for each member a deputy. The Committee shall adopt rules of procedure for itself and shall elect a chair from among its members. The number of members shall not exceed 21. The rules of procedure and the election of the chair are subject to the approval of the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour.
(5) The Federal Ministry and the supreme State ('Land') and higher Federal authorities responsible for health and safety are entitled to be represented and heard in the meetings of the Committee.
(6) The business of the Committee shall be conducted by the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
(1) To protect employees and third parties form hazards arising from installations which require special inspection in view of their hazardous nature (installations subject to mandatory inspection) the Federal Government shall be authorised, after hearing the groups involved, to determine the following by statutory ordinance with the consent of the Bundesrat:
| 1 | that notification be given of the erection of such installations, their commissioning, the implementation of modifications to existing installations and other circumstances affecting the installations and that the notification be accompanied by certain documents; |
| 2 | that the erection of such installations, their Operation and the implementation of modifications to existing installations be subject to permission form an authority named in the statutory ordinance or responsible under Federal or State ('Land') law; |
| 2a | that such installations or parts of such installations may be generally approved after a type approval test and that the general approval may involve conditions for Operation and maintenance; |
| 3 | that such installations, especially their erection, manufacture, type, materials, equipment and maintenance and their Operation, have to satisfy certain requirements which accord with the state of the art; |
| 4 | that such installations be subject to a pre-commissioning inspection, regular in-service inspections and inspections based on official Orders. |
(2) In the statutory ordinances under Subsection 1 regulations may be established concerning the assignment of technical committees. The committees shall advise the Federal Government or the competent Federal Ministry in technical matters. They propose rules in accordance with the state of the art (technical rules), taking due account of the rules for other protective goals and, where its areas of responsibility are affected, in consultation with the Technical Committee for Plant Safety according to Section 31 a Subsection 1 of the Federal Law for the Protection against Emissions ('Bundes-lmmissionsschutzgesetz'). In addition to representatives of the Federal authorities and supreme State ('Land') authorities involved and of the approved inspection bodies in the meaning of Section 17, in particular representatives of employers, trade unions and statutory accident Insurance bodies shall be appointed to the committees.
(3) Technical rules may be published by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour.
(4) Permits according to a statutory ordinance under Subsection 1 No. 2 shall expire if the owner has not commenced erection of the Installation within a period of two years from issuance of the permit, Interrupts construction work for two years or does not operate the Installation for a period of three years. The period may be extended for an important reason on application from the permitting authority.
(1) The competent authorities may, in individual cases, order the necessary measures for the implementation of the obligations imposed by the statutory ordinance under Section 14. It may also order the measures needed in individual cases to ward off hazards for employees or third parties.
(2) The competent authority may order the shut-down or disposal of an Installation which has been erected, operated or modified without the permission required on the basis of a statutory ordinance according to Section 14 Subsection 1 No. 2 or 4 without inspection by an approved inspection body.
(3) In the case of Orders under Subsection 1 the competent authority may prohibit Operation of the Installation concerned until a condition which accords with the Orders is achieved. The same applies if an order is established according to other regulations concerning the facility or workplace in which the Installation is operated.
Possessors of installations subject to mandatory inspection and persons who manufacture or operate such installations are obliged to make the installations accessible on demand to the representatives of approved inspection bodies responsible for inspection the installations, to permit the inspection prescribed or officially ordered, to make available the necessary labour and aids for this purpose and to give them details and submit documents to them. The basic right of Article 13 of the Basic Law ('Grundgesetz') is thereby limited.
(1) The inspections on installations subject to mandatory inspection shall be performed by approved inspection bodies where nothing different is provided for in the statutory ordinances under Section 14 Subsection 1.
(2) For installations subject to mandatory inspection the following can determine which bodies will perform the inspection and surveillance:
(3) The Federal Government can determine in the statutory ordinances under Section 14 Subsection 1, with the consent of the Bundesrat, the requirements which the approved inspection bodies under Subsection 1 must satisfy beyond the general requirements for an accreditation given in Subsection 5.
(4) The State ('Land') Governments can do the following by way of statutory ordinances:
The statutory ordinances under Sentence 1 can also be the basis for the obligations of the approved inspection bodies
(5) An approved inspection body is any inspection body named by the competent State ('Land') authority to the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour as an inspection body for a certain area of work and published by the latter in the Bundesanzeiger (Federal Gazette). The inspection body can be named as such if it has been ascertained in an accreditation procedure that compliance with the following general requirements and the special requirements given in a statutory ordinance under Section 14 Subsection 1 is guaranteed:
Inspections bodies of companies or groups of companies may also be appointed as approved inspection bodies without fulfilling the requirements under Sentence 2 No. 1, especially for the Implementation of legal acts of the Council or Commission of the European Communities concerning subject areas of the present Act, provided this is provided for in a statutory ordinance according to Section 14 Subsection 1 and the requirements laid down there are met.
(6) The accreditation may be granted under certain conditions and may involve specific stipulations. It may only be granted for a limited term and may be granted subject to revocation and subsequent stipulations. Issuance, expiry, withdrawal, revocation and cancellation shall be notified without delay to the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour.
(7) The accreditation of approved inspection bodies is the task of the competent authority under State ('Land') law. The competent authority monitors compliance with the general requirements given in Subsection 5 Sentence 2 and the special requirements given in a statutory ordinance under Section 14 Subsection 1. It may demand of the approved inspection body and the latter's personnel assigned to manage and implement the specialist tasks the Information and support required to perform the monitoring tasks and it may issue Orders required for this purpose. Its delegated representatives are empowered to enter and inspect sites and business premises during the operational and business hours and to demand presentation of documents for the issuance of the certificates. Those obliged to prove Information shall accept the measures according to Sentence 4.
(8) The competent authority responsible for implementing the statutory ordinances passed under Section 14 Subsection 1 may demand of the approved inspection body and the latter's personnel assigned to manage and implement the specialist tasks the Information and support required to perform the monitoring tasks and it may issue Orders required for this purpose. Its delegated representatives are empowered to enter and inspect sites and business premises during the operational and business hours and to demand presentation of documents for the issuance of the certificates. If they become active under Sentences 1 and 2 they shall notify the competent authority responsible for the accreditation in the meaning of Subsection 5.
(1) The competent authorities under State ('Land') law are responsible for supervising the implementation of the statutory ordinances passed under Section 14 Subsection 1. Section 22 Subsections 1 and 2 and Section 23 Subsection 2 of the Occupational Safety and Health Act apply here accordingly.
(2) For installations subject to surveillance by the Federal administration, supervision may be delegated in statutory ordinances under Section 14 Subsection 1 to a Federal Ministry or the Federal Ministry of the Interior for a number of operative areas of the Federal administration; the Federal Ministry may delegate supervision to a body appointed by it. Section 48 of the Federal Waterways Act and Section 4 of the Federal Truck Roads Act are not affected.
(1) A person is committing an administrative offence if he/she acts as follows wilfully or negligently
(2) The administrative offence may, in the cases Subsection 1 No. 1 Letter a, Nos. 5, 6 Letter a and No. 9 be penalised by a fine of up to thirty thousand euro, and in the other cases by a fine of up to three thousand euro.
A person who persistently commits a wilful action described in Section 19 Subsection 1 No. 1 Letter a, No. 5 or 6 Letter a or who through such wilful action endangers the life or health of another or alien property of significant value will be punished by imprisonment for up to one year or by a fine.
(1) Until a statutory ordinance according to Section 3 Subsection 3 has been passed, an accreditation procedure according to Section 9 Subsection 2 Sentences 2 and 3 of the Equipment Safety Act in the version applying on 31 December 2000 shall be implemented when appointing an approved body.
(2) The inspections laid down on the basis of the statutory ordinances passed before 31 December 2000 according to Section 11 Subsection 1 of the Equipment Safety Act or officially ordered by authorities for installations subject to mandatory inspection by official or for this purpose officially recognised experts shall be performed by approved inspection bodies without prejudice to the provisions of Subsections 3 and 4 until relevant statutory ordinances come into force.
(3) Up to 31 December 2007 the technical inspection organisations recognised on the basis of statutory regulations of the State ('Land') Governments according to Section 14 Subsection 4 of the Equipment Safety Act before 31 December 2000 can operate and experts can be officially recognised for the inspection of installations subject to mandatory inspection. In this period the statutory regulations mentioned in Sentence 1 shall apply accordingly; exceptions are provisions by which technical inspection organisations are obliged to grant their experts a salary adjusted to that of the comparable state officials ('Beamten') or employees of the State ('Land') or Federal administration and Provision for old age, surviving dependants and invalidity.
(4) Up to 31 December 2007 the inspections by approved inspection bodies on installations subject to mandatory inspection prescribed on the basis of statutory ordinances passed according to Section 11 Subsection 1 of the Equipment Safety Act in the version valid on 31 December 2000 or officially ordered by authorities can be performed by official experts or for this purpose officially recognised experts. Sentence 1 applies as appropriate for experts authorised on the basis of a statutory ordinance passed before 31 December 2000 according to Section 11 Subsection of the Equipment Safety Act to perform prescribed or officially ordered inspections on installations subject to mandatory inspection. For the inspections by official or officially recognised experts as mentioned in Sentence 1 fees and expenses shall be charged; for this purpose the costs ordinance for the inspection of installations subject to mandatory inspection of 23 November 1992 (BGBI. l P. 1944), amended by the ordinance of 15 April 1996 (BGBI. l P. 611), continues to apply. The Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour is empowered to change by statutory ordinance the fees and expenses of the costs ordinance for the inspection of installations subject to mandatory inspection after hearing the groups involved with the consent of the Bundesrat.
(5) The inspections on installations subject to mandatory inspection by approved inspection bodies prescribed on the basis of statutory ordinances passed according Section 14 Subsection 1 or officially ordered by authorities may be performed until 31 December 2005 only by official or for this purpose officially recognised experts. Where the installations subject to mandatory inspection
the inspections mentioned in Sentence 1 may only be performed until 31 December 2007 by experts mentioned in Sentence 1. Subsection 4 Sentence 2 applies accordingly. Subsection 4 Sentence 3 applies.
Article 2
Amendment of the Act on the Establishment of a Federal Motor Vehicles
Department ('Kraftfahrt-Bundeamt')
Section 2 Subsection 1 of the Act on the Establishment of a Federal Motor Vehicles Department in the adapted version published in the Federal Law Gazette (Bundesgesetzblatt) Part IM, Number 9230-1, which was last amended as follows by Article 3 of the Act of 12 December 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2518) is amended is follows:
Article 3
Amendment of the Ship Safety Act
In Section 1 Subsection 3 No. 6 of the Ship Safety Act of 9 September 1998 (BGBI. l P. 2860), last amended by Article 2 of the ordinance of 8 December 2003 (BGBI. l PP. 2465, 2766), the words "Equipment Safety Act and according to the Product Safety Act" are replaced by the words "Equipment Safety Act and Product Safety Act".
Article 4
Amendment of the BfR Act (Law on the Establishment of a Federal
Institute for Risk Evaluation)
In Section 2 Subsection 1 No. 12 of the BfR Act of 6 August 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3082) the word "Product Safety Act" is replaced by the words "Equipment and Product Safety Act".
Article 5
Amendment of the BVL Act
(Law on the Establishment of a Federal Department for Consumer
Protection and Food Safety)
Section 2 of the BVL Act of 6 August 2002 (BGBI. l PP. 3082, 3084) is amended as follows:
Article 6
Amendment of Water Resources Management Act
In Section 19f Subsection 1 Sentence 1 of the Water Resources Management Act in the version of the notice of 19 August 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3245) the indication "Section 2 Subsection 2a of the Equipment Safety Act" is replaced by the indication "Section 2 Subsection 7 of the Equipment and Product Safety Act".
Article 7
Amendment of the Federal Law for the Protection against Emissions
The Federal Law for the Protection against Emissions is the version of the notice of 26 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3830) amended by Article 41 of the ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304) is amended as follows:
Article 8
Amendment of the Nuclear Act
The Nuclear Act in the version of the notice of 15 July 1985 (BGBI. l P. 1565), last amended by Article 125 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304) is amended as follows:
Article 8a
Amendment of the Construction Products Act
Section 13 of the Construction Products Act in the version of the notice of 28 April 1998 (BGBI. l P. 812), last amended by Article 4 of the act of 15 December 2001 (BGBI. l P. 3762) is amended as follows:
Article 9
Amendment of the Inland Shipping Inspection Code
In Section 4a Subsection 1 Sentence 2 of the Inland Shipping Inspection Code of 17 Manch 1988 (BGBI. l P. 238), last amended by Article 2 of the ordinance of 28 February 2001 (BGBI. l P. 335), the words "Section 2 Subsection 3 of the Equipment Safety Act in the version of the notice of 23 October 1992 (BGBI. l P. 1793), which was amended by the act of 27 April 1993 (BGBI. l P. 512)" are replaced by the indication "Section 2 Subsection 8 of the Equipment and Product Safety Act of 6 January 2004 (BGBI. l P. 2).".
Article 10
Amendment of the Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of
Electrical Equipment for Use within Certain Voltage Limits
The Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Electrical Equipment for Use Within Certain Voltage Limits of 11 June 1979 (BGBI. l P. 629) amended by Article 1 of the ordinance of 28 September 1995 (BGBI. l P. 1213) is amended as follows:
Article 11
Amendment of the Ordinance on the Safety of Toys
The Ordinance of the Safety of Toys of 21 December 1989 (BGBI. l P. 2541), last amended by Articie 308 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304), is amended as follows:
Article 12
Amendment of the Machine Noise Information Ordinance
The Machine Noise Information Ordinance of 18 January 1991 (BGBI. l P. 146), last amended by Article 2 Subsection 3 of the Ordinance of 12 May 1993 (BGBI. l P. 704), is amended as follows:
Article 13
Amendment of the Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Simple
Pressure Vessels
The Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Simple Pressure Vessels of 25 June 1992 (BGBI. l P. 1171), last amended by Article 309 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304), is amended as follows:
Article 14
Amendment of the Gas Consumption Devices Ordinance
The Gas Consumption Devices Ordinance of 26 January 1993 (BGBI. l P. 133), as amended by Article 5 of the Ordinance of 28 September 1995 (BGBI. l P. 1213), is amended as follows:
Article 15
Amendment of the Ordinance on the bringing into Circulation of Personal
Protective Equipment
The Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Personal Protective Equipment in the version of the notice of 20 February 1997 (BGBI. l P. 316) is amended as follows:
Article 16
Amendment of the Machinery Ordinance
The Machinery Ordinance of 12 May 1993 (BGBI. l P. 704), last amended by Articie 6 of the Ordinance of 28 September 1995 (BGBI. l P. 1213), is amended as follows:
Article 17
Amendment of the Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of
Recreational Craft
The Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Recreational Craft of 18 December 1995 (BGBI. l P. 1936) is amended as follows:
Article 18
Amendment of the Explosion Protection Ordinance
The Explosion Protection Ordinance of 12 December 1996 (BGBI. l P. 1914), last amended by Article 5 Subsection 1 of the Ordinance of 27 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3777), is amended as follows:
Article 19
Amendment of the Lifts Ordinance
The Lifts Ordinance of 17 June 1998 (BGBI. l P. 1393), last amended by Article 5 Subsection 2 of the Ordinance of 27 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3777), is amended as follows:
Article 20
Amendment of the Aerosol Dispensers Ordinance
The Aerosol Dispensers Ordinance of 27 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3777, 3805) is amended as follows:
Article 21
Amendment of the Pressure Equipment Ordinance
The Pressure Equipment Ordinance of 27 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3777, 3806) is amended as follows:
Article 22
Amendment of the Plant Safety Ordinance
The Plant Safety Ordinance of 27 September 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3777), amended by Article 306 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304), is amended as follows:
Article 22a
Amendment of the Ordinance on Installations Subject to Mandatory
Inspection
Number 9.1 of the appendix to the Ordinance on Installations Subject to Mandatory Inspection in the version of the notice of 14 March 1997 (BGBI. l P. 504), last amended by Article 3 of the Ordinance of 14 August 2003 (BGBI. l P. 1614), is amended as follows:
Article 23
Amendment of the Equipment and Machine Noise Control Ordinance
The Equipment and Machine Noise Control Ordinance of 29 August 2002 (BGBI. l P. 3478) is amended as follows:
| 1 | Section 6 is amended as follows:
|
| 1a | In Section 7 Subsection 2 Sentence 4 the words "or otherwise in the public interest" are inserted after the word "General". |
| 2 | In Section 9 Subsection 1 is replaced by the following
Subsections 1 and 1a: "(1) A person is committing an administrative offence in the meaning of Section 19 Subsection 1 No. 1 Letter a of the Equipment and Product Safety Act if he/she acts as follows wilfully or negligently
|
Article 24
Amendment of the General Mining Ordinance
In Section 18 Subsection 1 Sentence 2, Section 18 Subsection 3 No. 1 and Section 18 Subsection 5 Sentence 2 of the General Mining Ordinance of 23 October 1995 (BGBI. P. 1466), as amended by Article 1 of the Ordinance of 10 August 1998 (BGBI. P. 2093), the words "the Eighth Ordinance to the Equipment Safety Act" are replaced in each case by the words "the Ordinance on the Bringing into Circulation of Personal Protective Equipment".
Article 25
Amendment of the Ordinance on High-pressure Gas Pipelines
The Ordinance on High-pressure Gas Pipelines of 17 December 1974 (BGBI. l P. 3591), last amended by Article 276 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304), is amended as follows:
Article 26
Amendment of the Second Ordinance to Adjust the List of Fees of the
Schedule of Costs for the Inspection of Installations Subject to
Mandatory Inspection
In Section 1 of the Second Ordinance to Adjust the List of Fees of the Schedule of Costs for the Inspection of Installations Subject to Mandatory Inspection of 24 October 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2105) the words "Section 19 Subsection 6 Sentence 3 of the Equipment Safety Act in the version of the notice of 11 May 2001 (BGBI. l P. 866)" are replaced by the indication "Section 21 Subsection 4 Sentence 3 of the Equipment and Product Safety Act of 6 January 2004 (BGBI. l P. 2)".
Article 27
Return to Uniform Ordinance Status
The parts of the statutory ordinances based on Articles 9 to 26 and amended there may be amended by statutory ordinance on the basis of the relevant authorisations in each case.
Article 28
Corning into Force, Cessation of Validity
The present Act comes into force on the first day of the fourth calendar month following its promulgation. At the same time the Equipment Safety Act in the version of the notice of 11 May 2001 (BGBI. l P. 866), last amended by Article 182 of the Ordinance of 25 November 2003 (BGBI. l P. 2304), and the Product Safety Act of 22 April 1997 (BGBI. l P. 934), last amended by Article 7 of the Act of 11 October 2002 (BGBI. P. 3970) cease to be valid.
| ° Top of Page | × Statutes | ¤ Homepage | «« Previous page |
© for this translation 2004 Bundesanstalt
für Arbeitsschutz und Arbeitsmedizin
This HTML edition by Pauline Vilentschuk and © 2006 Gerhard Dannemann. The
contents of this page may be downloaded and printed out in single
copies for individual use only. Making multiple copies without
permission is prohibited.